You cover a lot of ground in genomics; every day there are so many exciting things happening! Lab automation technology is one of the important tools that scientists use. This technology aids scientists in speeding up their work and being more accurate by automating routine tasks. Follow how lab automation is transforming genomics research!
DNA sequencing is essential to genomics studies. It helps scientists learn about the genes that make up living things like humans. But the conventional method for sequencing DNA can be slow and has errors. This is where lab automation technology comes to the rescue!
But lab automation technology helps DNA sequencing go faster. It automates challenges like preparing samples, calibrating equipment, and analyzing data. This means researchers can spend more time analyzing results and discovering new findings. It is a time saver and ensures accuracy in the results.
Automation allows scientists to analyze large quantities of data very quickly and with high precision. This is the case in genomics research, where the amount of data to sift through can be quite large. Automation of data analysis allows researchers to discover patterns and insights that they wouldn’t otherwise discover by working through everything, by hand.
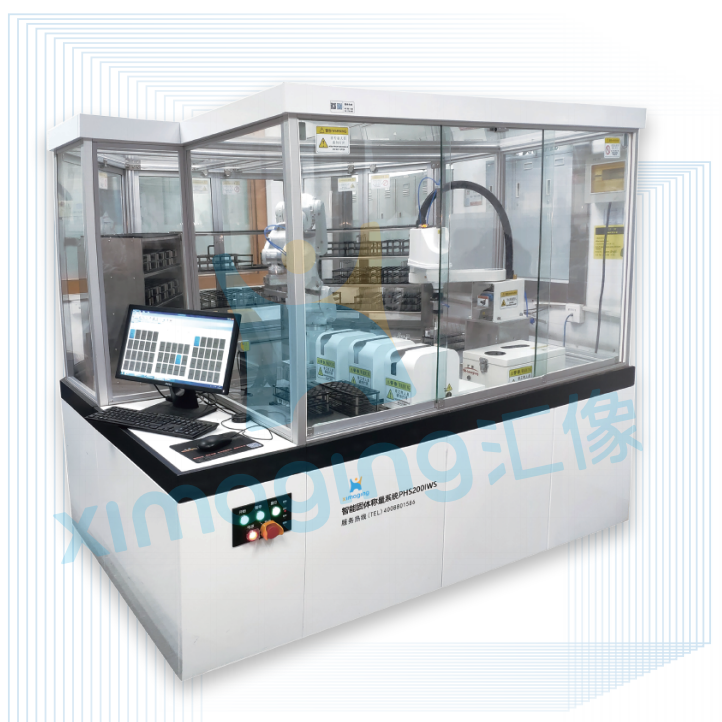

Automation plays a very crucial role in genomics labs to enhance productivity and accelerate research. By automating processes including sample preparation, DNA extraction and analysis, scientists can concentrate on more challenging aspects of their work.
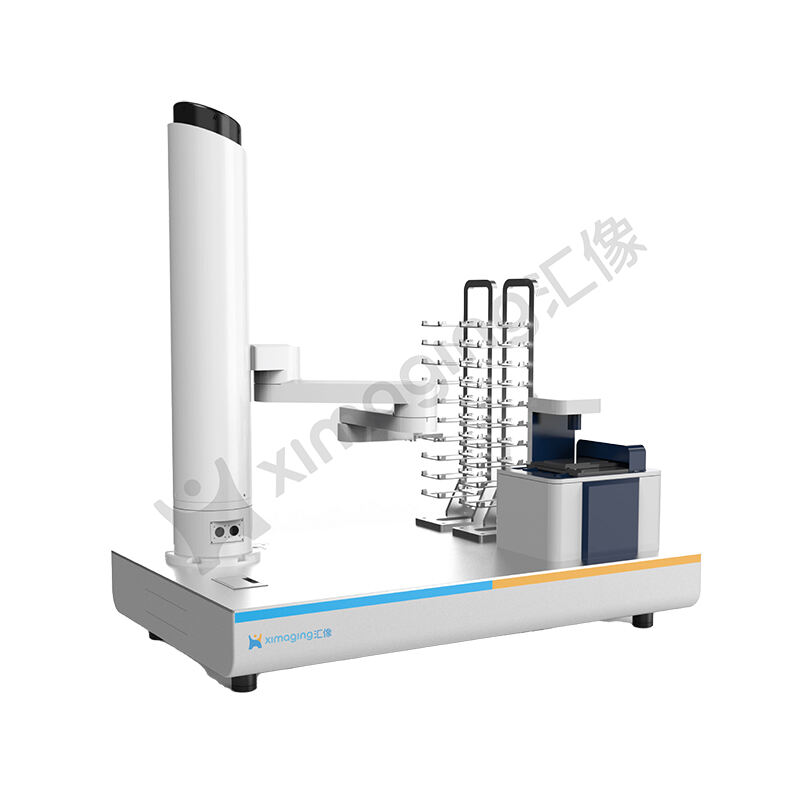

Automation also empowers labs to operate smoothly. With machines handling boring tasks, scientists can juggle many projects. It does mean they can find out more and work more effectively. Automation is an essential aspect of success in genomics labs across the globe.
Genomics researchers can accelerate discoveries by automating everyday tasks. Lab automation technology helps scientists process samples, analyze data, and retrieve results more quickly than ever before. Translation: It lets you do more experiments and collect more data, contributing to major genomics breakthroughs.